As AI servers rapidly evolve toward higher power, greater density, and more modular architectures, electrical safety testing is no longer a routine end-of-line inspection. Instead, it has become a critical factor that directly affects product launch timelines and global market competitiveness.
When undergoing safety compliance testing, products must not only complete fundamental tests, such as hipot (dielectric withstand), insulation resistance, ground bond, and leakage current, but also perform multi-point testing at various locations to meet the verification requirements of international standards like IEC 62368-1. On the production floor, we have observed that AI server manufacturers commonly face the following three major pain points:
1. Multiple Test Points and Combinational Verifications Make Test Processes Difficult to Simplify
The first challenge lies in the complexity introduced by frequent switching between multiple test points. AI servers feature highly integrated power architectures and signal modules, requiring test coverage across various combinations such as input-to-ground, output-to-ground, and input-to-output. This results in a large number of hipot and insulation resistance test points.
Test operators must constantly change measurement points and wiring configurations, which not only increases operation time but also makes it difficult to standardize the overall testing process. As a result, production lines take more time and mass-production efficiency is negatively impacted.
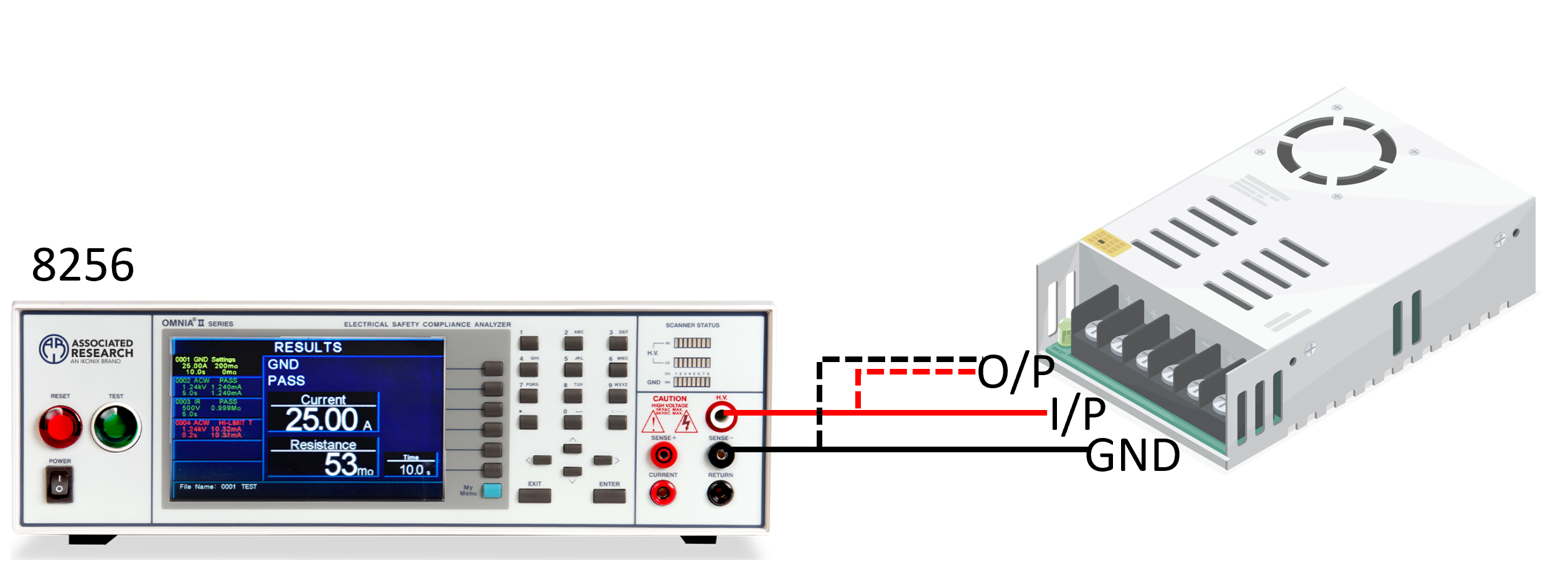
2.Heavy Reliance on Manual Operation Raises Risks and Consistency Concerns
The second pain point stems from the heavy reliance on manual operations, which introduces both safety risks and quality consistency issues. During manual switching of test points, problems such as poor contact, loose cables, or incorrect connections occur frequently. Minor issues may lead to test failures and retesting, while more serious cases could result in false passes, creating hidden quality and compliance risks.
In addition, the frequent handling and reconnection of high-voltage test leads poses challenges to operator safety and increases operational stress. This becomes an even greater concern for production lines that require prolonged testing cycles.
3.Increasing Pressure on Test Data and Report Management to Meet Audit and Traceability Requirements
The third common pain point arises from the growing demands for test data management and auditing. AI servers are typically high-value, highly-customized products, and customers as well as third-party certification bodies often require complete and fully traceable test records.
If data is still managed through manual transcription or fragmented storage, the process becomes time-consuming and prone to errors or omissions. Some manufacturers are also required to generate printable, tamper-proof test reports in real time to support internal audits, external inspections, and customer validation which further increases testing and administrative costs.
Manufacturers Must Prioritize Test Efficiency and Data Integrity
In summary, the challenges AI server manufacturers face during electrical safety testing are no longer limited to simply “passing the test.” The real issue is how to ensure safety and compliance while simultaneously achieving efficiency, stability, and data integrity. These pain points highlight the core issues that the industry must address when adopting more advanced testing systems and automated solutions.
For a deeper look into AI server market trends and relevant international electrical safety standards, we invite you to read: AI Server Technology Evolution: How Can Server Manufacturers Achieve International Electrical Safety Compliance Amid Rapid Innovation?





