

EV Battery Relevant Standards
Batteries are series-parallel connected to increase the voltage up to 300V on the battery pack to enhance endurance. This is much higher than the Safety Extra Low Voltage (SELV, < 60Vdc), so the battery pack’s electrical safety needs additional attention.

A battery pack is composed of several battery modules, and each battery module is composed of several cells. If the battery modules and cells have any defaults, it may damage the battery pack and have potential safety concerns. Therefore, most manufacturers conduct insulation resistance (IR) tests on the cells to ensure no foreign particles and damage in the inner insulation layer. Follow by the Hipot test between the battery module’s terminals and the chassis to ensure the assembly and structure are safe.
The complete battery pack must pass the UL 2580 electrical safety test. The following are electrical safety test criteria:
- IR test
If the insulation capability is inadequate, insulation failure may occur to damage the battery. Therefore, use the maximum working voltage (usually 300Vdc to 600Vdc) to conduct the IR tests for 60 seconds. The IR value must be greater than 100 ohms/Vdc (usually 30000 ohms to 60000 ohms in total).
- Hipot Test
By ensure the battery packs’ structure and assembles properly can avoid insulation failure occurs. So, conduct the Hipot test with twice rated DC voltage (usually 600 Vdc to 1200Vdc) for 60 seconds. After the test, the DUT should not breakdown.
The testing methods show in the following diagram. The testing voltage applies in turns to the battery’s terminals and the return lead connect chassis.
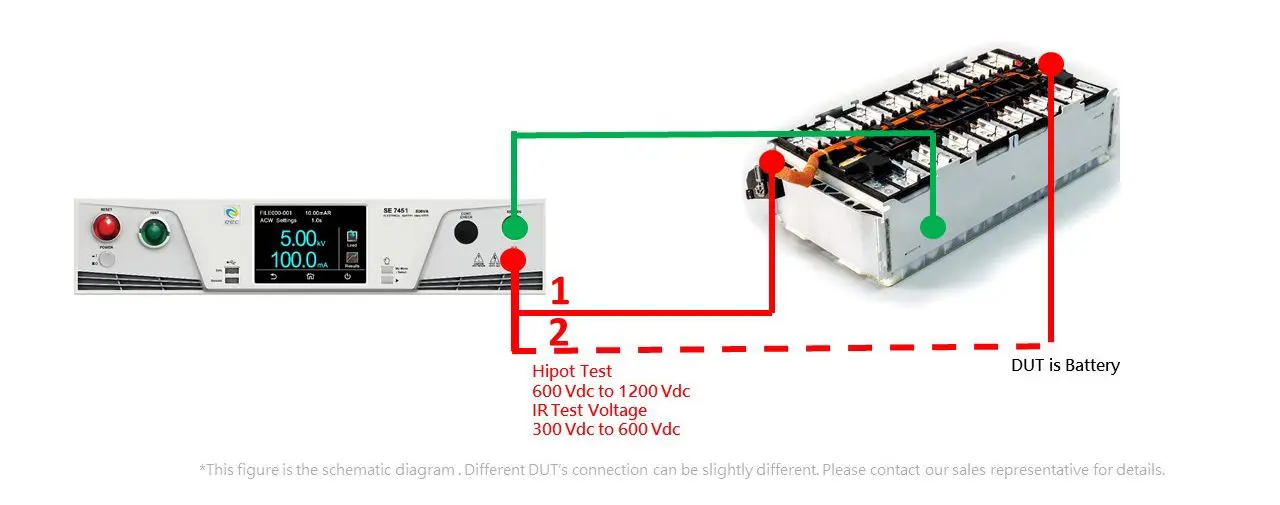
Figure 1: UL 2580 EV Battery Pack Safety Testing Configuration
In China, the EV battery pack must comply with GB 38031 to conduct the IR test. Apply a large DC voltage to terminals in turn, and measure the IR value between terminals and chassi. The test method shows in Figure 2. The testing voltage is 500Vdc or 1.5 times rated voltage (usually up to 900Vdc) for 60 seconds. The testing result should be greater than 100 ohm/V (normally around 30000 ohms to 60000 ohms).
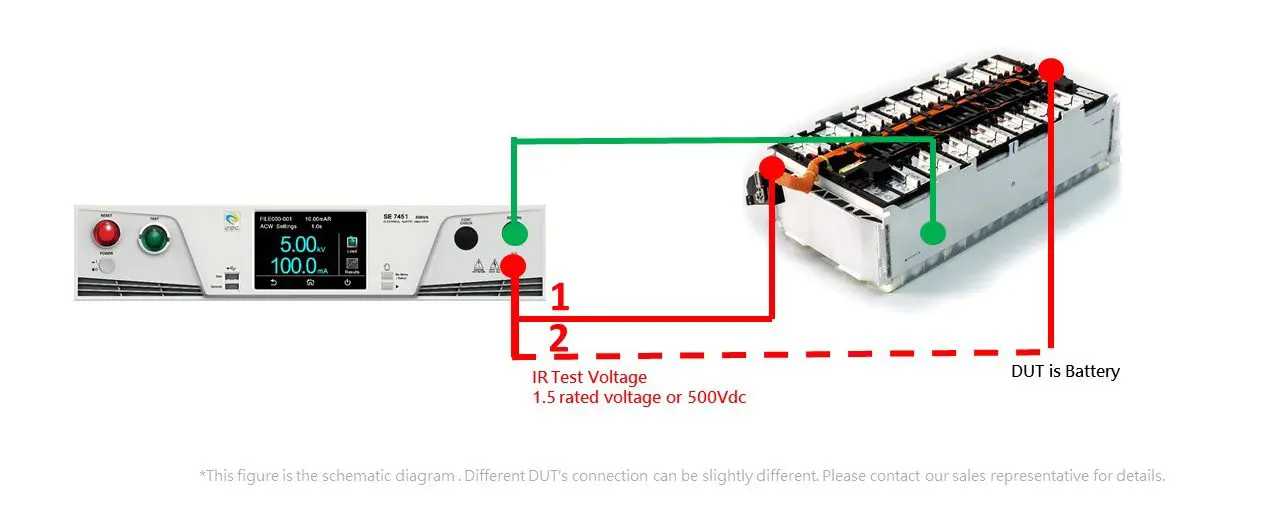
Figure 2: GB 38031 EV Battery Pack Safety Testing Configuration
Ikonix Offers Completed Test Solutions
For the electrical safety testing of the EV batteries, legendary SE Series Electrical Safety Analyzer is your best choices. SE series have AC/DC Hipot and IR test functions. The maximum output can reach 500 VA which meets the UL’s safety tests’ requirements. Along with the battery packs’ voltage continually increase, the SE series provides up to 5kVac and 6kVdc for the Hipot test and 6kVdc for IR tests to meet the R&D and labs’ needs.
The EV era is evolving. Ikonix works closely with industry-leading companies to help the development and safety of EVs. With more than 80 years of safety testing industry experience, we provide complete testing solutions for automakers and manufacturers. If you want to learn more about the EV industry solutions, issue 16 and 19 has more testing information of motor and charging stations. Or you can contact our sales representatives to learn the complete solution now.




