The pandemic has shift consumer behavior from in-store to online. Boosting the e-commerce industry as well as the demand for the logistic industry. In China, compared to 2019, the total deliveries were made in 2020 raised by 30.8%1and continue to grow. While this brings convenience to human lives, the logistic industry also contributes a large amount of carbon emissions and causes a significant impact on the environment. Therefore, the logistics and truck manufacturers actively looking for a solution that can be balanced between eco-friendly, energy-efficient, and economic development. In the recent news, the three major European truck manufacturers, Daimler Trucks, AB Volvo, and Traton, have worked together to develop the charging network for long-distancing electric trucks and buses.2 The electric truck is the new trend, but “range anxiety” continues to be the biggest concern. Therefore, before electric trucks can get to the mainstream, it is necessary to set up a complete charging network. In addition, an electric truck requires greater energy and power than a smaller electric vehicle, the safety of the charging station are stricter.
Introduction to Charging Station Safety Testing Methods
Before building a complete charging network infrastructure in eliminating the "range anxiety", it is necessary to ensure each charging station complies with international regulations. In Figure 1 shows three case of charging stations. No matter which case, they have to conduct the safety test on power source input and output, plug, connector and sockets. The relevant standards are IEC 61851 (charging station) and IEC 62196 (plug, connector and sockets). In the following, we have further introduced those standards and testing methods.

Figure 1: 3 Cases of Charging Station
IEC 61851 (Requirements for electric vehicle conductive charging system) is specific for the charging station itself. We have introduced details back in issue 11, below is a quick review of the testing criteria and methods:
Hipot test
In general, the testing voltage is up to 2.2 kVac (or 3.1kVdc). For referenced insulation charging station, the testing voltage is up to 4.4 kVac(or 6.2kVdc).
Insulation Resistance
Apply 500Vdc to carry out the test, this voltage injects into the input or output terminal. The return lead connects to the chassis. The result should greater than 1M Ω.
Leakage current
To conduct the test, the testing voltage is 110% of the rated voltage. The leakage current should not exceed 3.5mA.
DC Grounding Bond
Inject 16A D.C. current, the resistance between exposed conductor and the earth should less than 0.1Ω.
The plug, connector, and sockets on the charging station/vehicle (shown in Figure 2) should comply with IEC 62196 (Standard for plugs, socket-outlets, vehicle connectors and vehicle inlets). The test criteria are Insulation Resistance, Hipot, and AC Ground Bond tests. The following has a complete description of the testing methods.
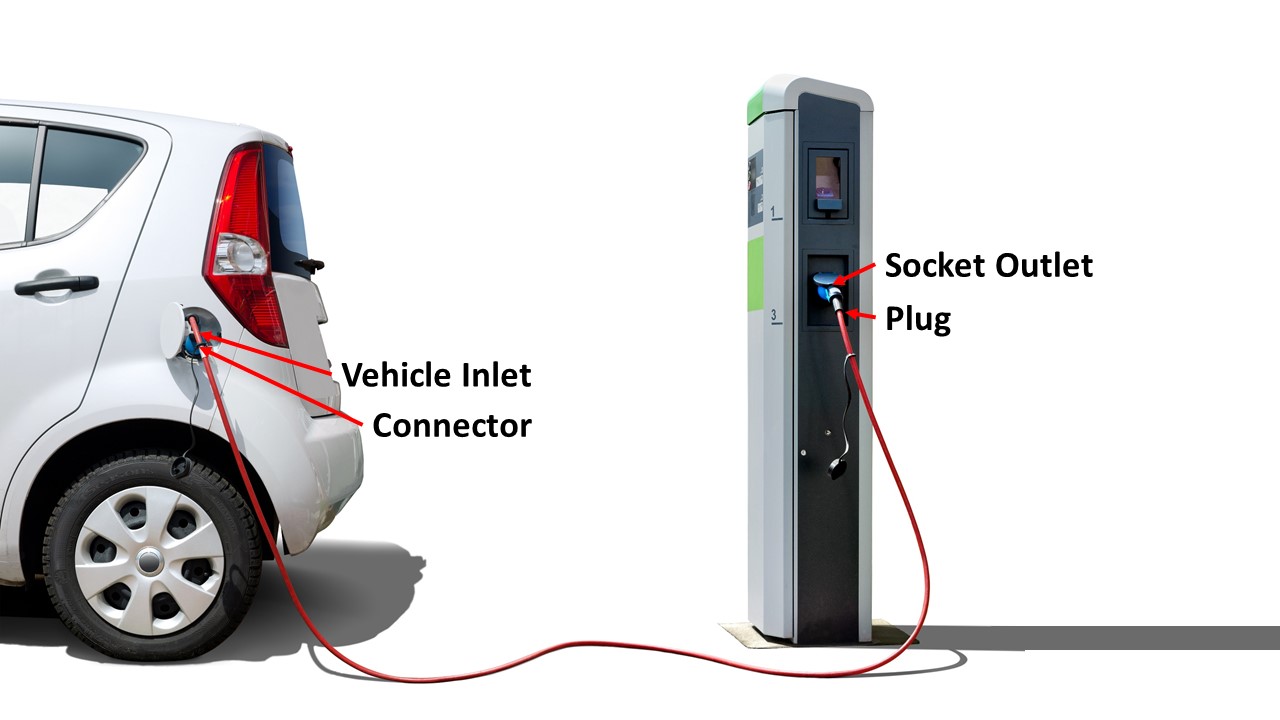
Figure 2: Plugs, Sockets and Connectors
Insulation Resistance
Normally, the testing voltage is 500 Vdc. If the rated voltage of the connection socket is over 500 Vac, then apply 1000 Vdc to conduct the test for 1 min. The final result of insulation resistance should greater than 5MΩ.
Hipot
According to the difference of insulation voltage that Device Under Test (DUT) can withstand, the testing voltage is varied. Table 1 summarized the testing voltage corresponds to the insulation voltage. Testing time is 1 minute and the DUT should withstand this high voltage without breakdown.
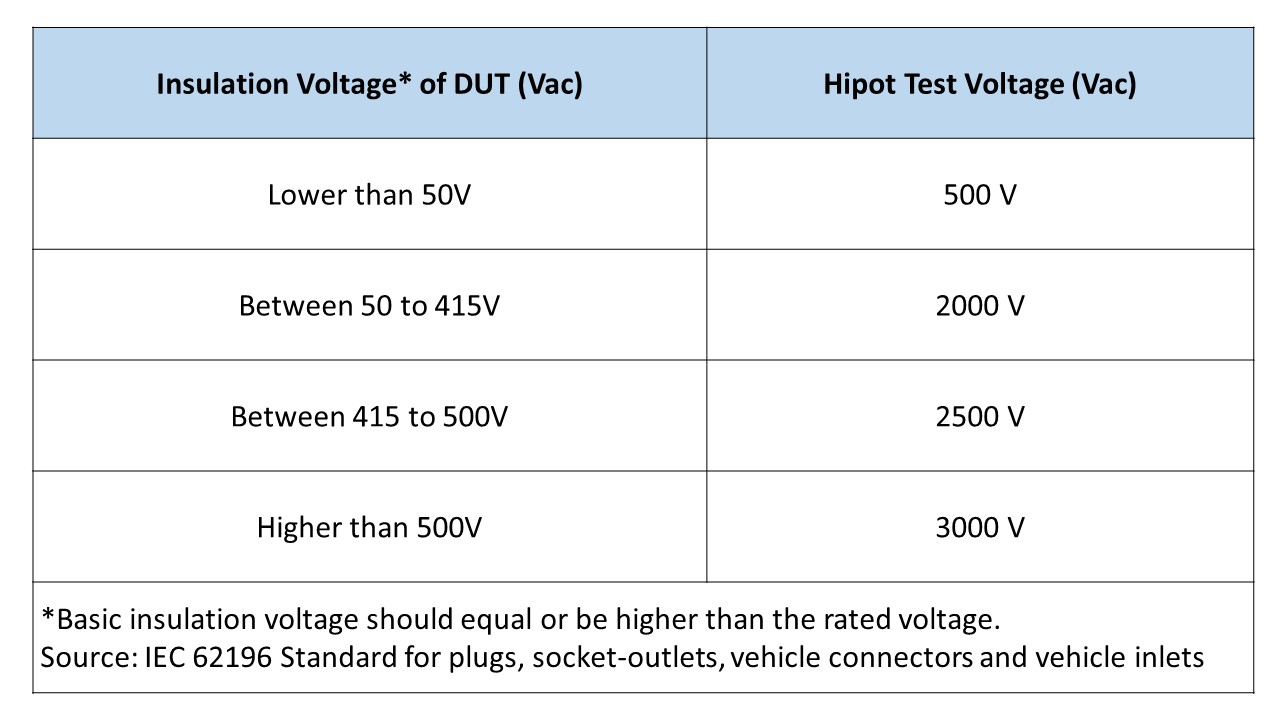
Table 1: IEC 62196 Socket, Connector, and Socket of Charging Station Hipot Test Voltage
Testing Methods
The type of plug, socket inlet and outlet on the charging station and vehicle, and connector varied in different countries because of the main electricity and local regulations. It can be divided into 2 to 4 poles. IEC 62196 Hipot and Insulation Resistance Test requires to conduct the following three methods (take 2 poles as an example):
- The HV lead of the safety tester connects to shorted poles. The return lead connection to the chassis.
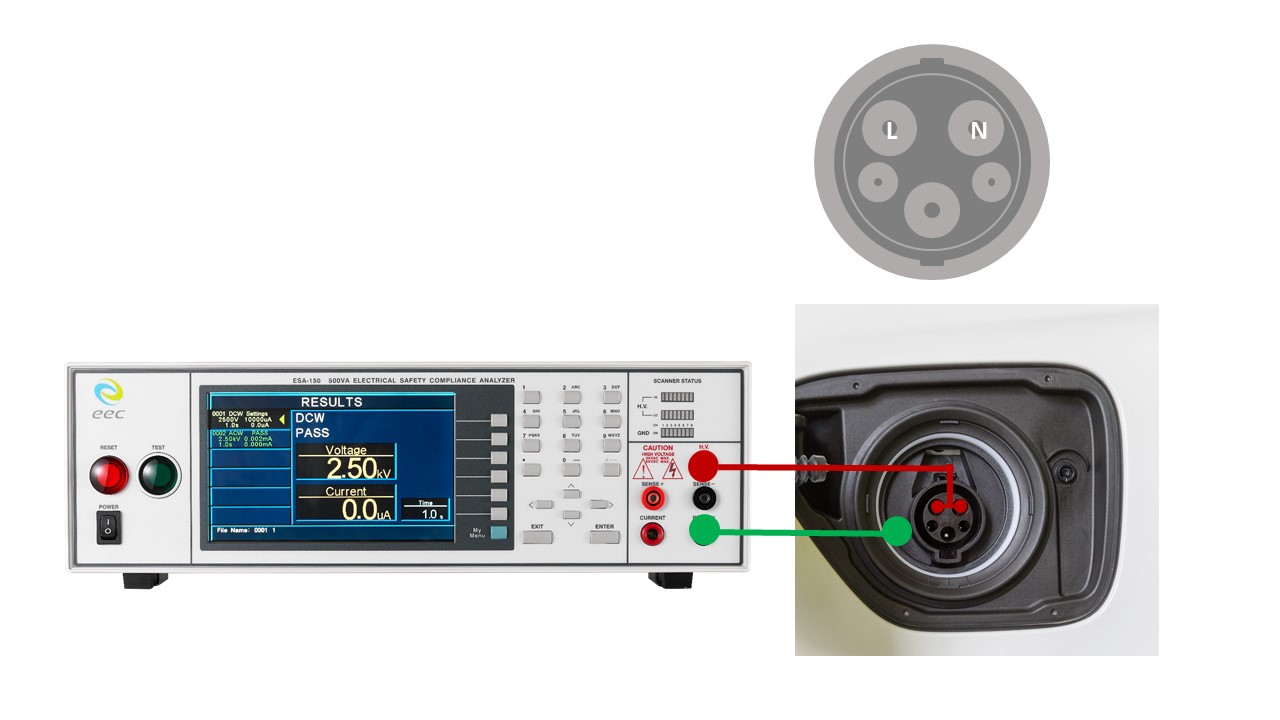
Figure 3: DUT Shorted-poles Connection - The HV lead of the safety tester connects to poles in turn. The return lead continually connects to the other poles.
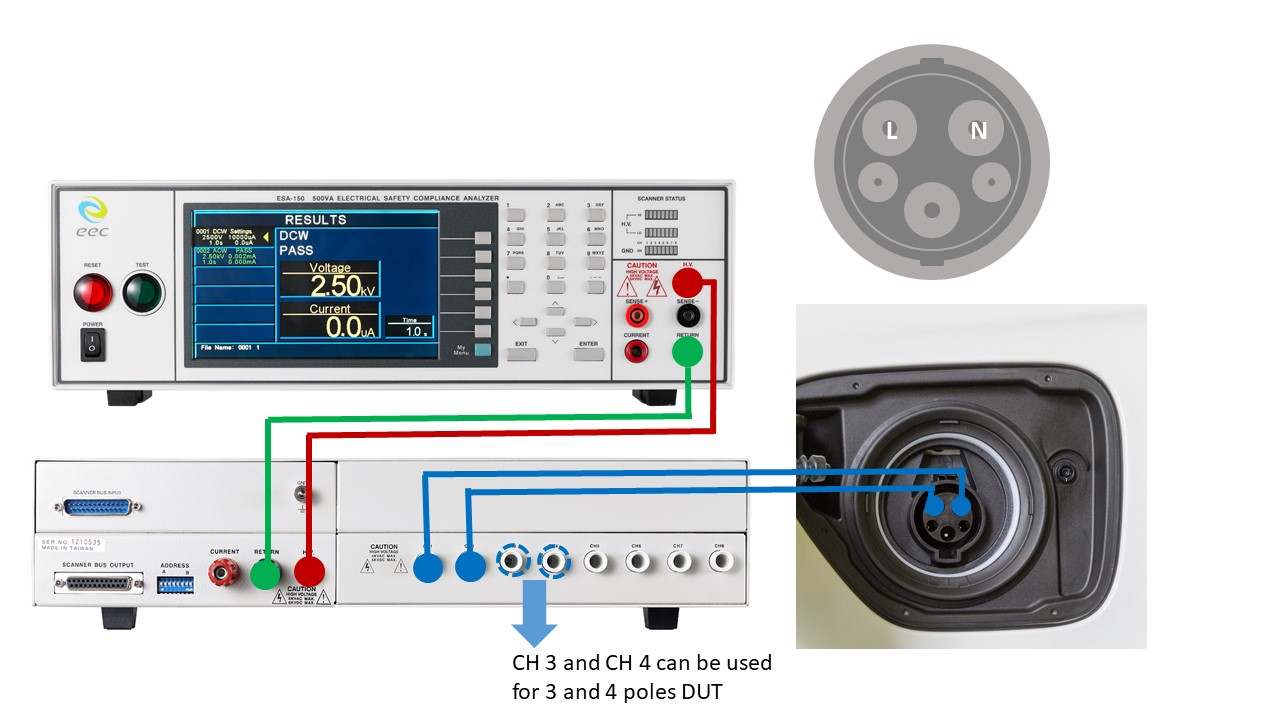
Figure 4: The Connection of Testing Poles in Turn - If the inner surface has the insulation lining, the return lead of the safety tester connects to the metal enclosure. The HV lead connects to the metal foil in contact with the inner surface of the insulation lining.
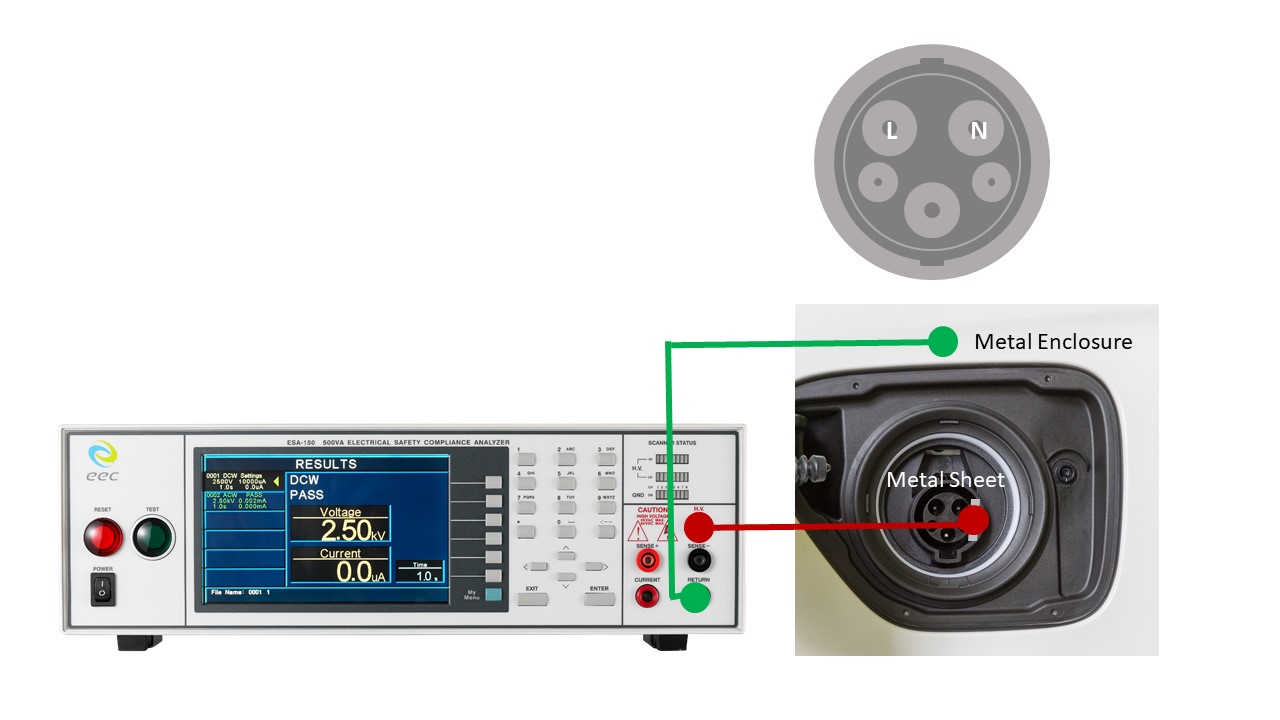
Figure 5: Connection of the Inner Insulation Testing
AC Ground Bond
If the DUT has any accessible metal part, it should conduct Ground Bond test. Inject 25A A.C. current to measure the resistance between accessible metal part and the earth is less than 0.1Ω.
Charging Stations Must Pass the Strict Safety Tests by Using High-quality Safety Testers
In the pandemic period, consumer behavior has gradually changed. This accelerates the innovation of logistics that incorporate low carbon-emission electrical vehicles (EVs). And charging stations plays an important role. Therefore, they must pass IEC 61851 and IEC 62196 standards to ensure their safety.
IEC 61851 required charging stations to conduct multiple electrical safety tests, it includes Hipot, Insulation Resistance, DC Ground Bond, and Leakage Current tests. And IEC 62196 has to conduct Hipot, Insulation Resistance, AC Ground Bond on multiple testing points on the DUTs. Customers purchase the ESA series safety tester with 7006 scanners, EGB-324 AC DC Ground Bond Tester, and EAL-5000 series AC source to bundle a complete charging station electrical safety testing solution.
ESA series provides up to 5kVac/6kVdc testing voltage for Hipot test and 1 kVdc for Insulation Resistance test. And the Fast Discharge function can discharge the DUTs in 50ms after the test to avoid accidental shock caused by the remaining voltage. Combining with 7006 Matrix Scanner can conduct the test on multiple testing points. Which resolves the complex cable connection conditions while simultaneously increase testing efficiency and productivity. EGB-324 AC/DC Ground Bond Tester provides up to 40A testing current. AC and DC Ground Bond tests are required by IEC 61851 and IEC 62196. EAL-5000 series Programmable AC Power Source provides a reliable power source to simulate the different real-world scenarios. Ikonix’s high-quality and high-accuracy testing solution can meet the high safety requirement of the EV industry.
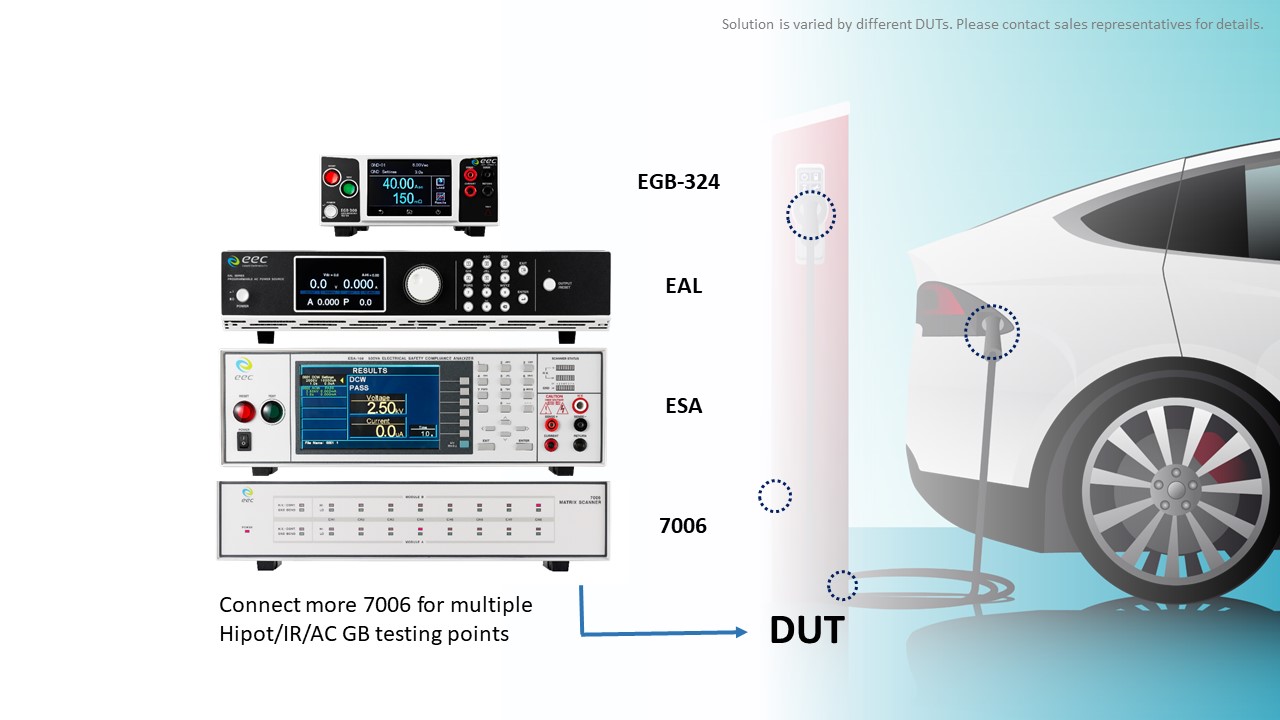
Figure 6: Ikonix Safety Tester and AC Source Charging Station Total Solution
Ikonix has been working closely with EV relevant manufacturers to ensure electrical safety. With more than 80 years of industry experience, we continually improve the quality and accuracy of our safety tester and AC sources. Have become the major laboratories and leading companies’ primary choice. If you are interested more in the electrical safety testing of an EV, we have a few more information about it in issue 11 and 16. If you would like to know more about Ikonix EV's electrical safety testing solutions, please contact our sales representative now.
References




